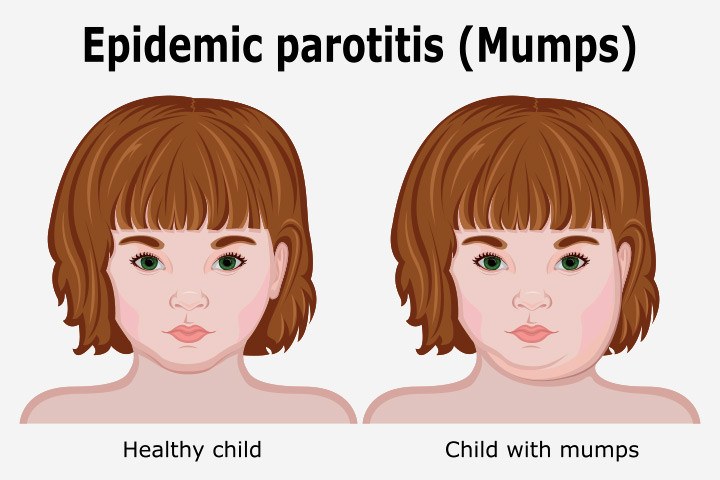
What is Parotitis or Mumps?
Parotitis, popularly called mumps, is a contagious viral disease, it can be acute or chronic, affecting one or both parotid glands, which are the salivary glands located behind the ascending branches of the jaw, behind the ears, causing febrile peaks from 39oc to 40oc and more.
The disease has an incubation time of 16 to 18 days and it is recommended to avoid sharing personal items, as it is transmitted through drops or saliva. It usually appears bilateral, but may be unilateral especially at the early stage of the disease, with pain during chewing or swallowing.
Complications of infection include orchitis, meningoencephalitis and pancreatitis. The diagnosis is usually based on clinical evaluation, where there is edema behind the ears, pain in the area, headache (headache), anorexia, malaise, among others. So when detecting any case should be notified to the Ministry of Public Health.
The treatment consists of supportive measures is symptomatic, rest, the patient should be isolated until the edema subsides, the diet should be soft, because it reduces the pain to chewing, avoiding the acidic substances that cause discomfort.
The prevention must be through vaccination that turns out to be effective.
Que es la Parotiditis o Paperas.
La Parotiditis, popularmente denominada Paperas, es una enfermedad viral contagiosa, puede ser aguda o crónica, que afecta a una o ambas glándulas parótidas, que son las glándulas salivales, ubicadas detrás de las ramas ascendentes de la mandíbula, detrás de los oídos, provoca picos febriles de 39oc a 40oc y más.
La enfermedad tiene un tiempo de incubación de 16 a 18 días y se recomienda evitar el uso compartido de artículos personales, ya que se transmite a través de las gotas o de saliva. Por lo general suele aparecer bilateral, pero puede ser unilateral sobre todo en la etapa inicial de la enfermedad, con dolor durante la masticación o deglución.
Las complicaciones de la infección incluyen orquitis, meningoencefalitis y pancreatitis. El diagnostico suele basarse en la evaluación clínica, donde aparece el edema detrás de los oídos, dolor en el área, cefalea (dolor de cabeza), anorexia, malestar general entre otras. Por lo que al detectarse algún caso debe notificarse al Ministerio de Salud Pública.
El tratamiento consiste en medidas de apoyo es sintomático, descanso, el paciente debe ser aislado hasta que el edema ceda, la dieta debe ser blanda, porque reduce el dolor a la masticación, evitando las sustancias acidas que causan molestias.
La prevención debe ser a través de la vacunación que resulta ser eficaz.